
Relational databases go together with the development of SQL.
This is because duplicate data not only waste storage spaces but also easily lead to inconsistencies.
A column name in a data table is associated with an attribute, an identifier or feature that all parts of a data set have. A large part of routine database administration involves evaluating all the data sets in a database to make sure that they are consistently populated and will respond well to SQL or any other data retrieval method.įor example, a conventional database row would represent a tuple, which is a set of data that revolves around an instance or virtual object so that the primary key is its unique identifier. Other issues with relational database designs include excessive duplication of data, faulty or partial data, or improper links or associations between tables. Inconsistencies can cause problems in how developers retrieve data. It must be unique for each member of a data set. Database administrators use Structured Query Language (SQL) to retrieve data elements from a relational database.Īs mentioned, the primary key is a fundamental tool in creating and using relational data models. There are also many free and open-source RDBMS, such as MySQL, mSQL (mini-SQL) and the embedded Java DB (Apache Derby).


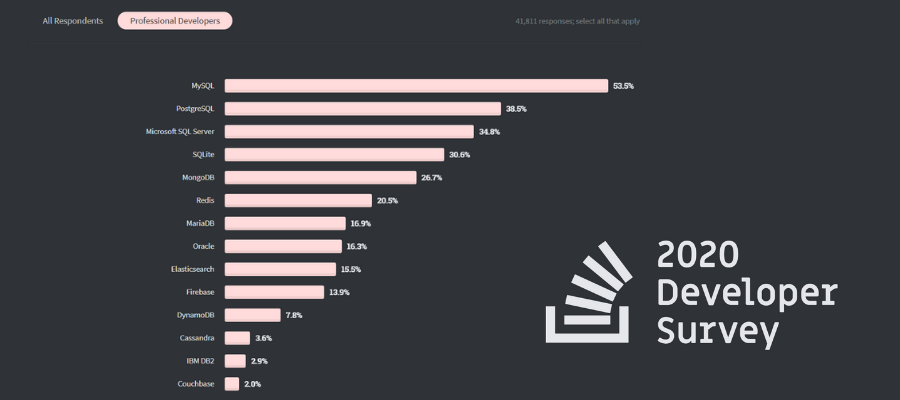
Today, there are many commercial Relational Database Management System (RDBMS), such as Oracle, IBM DB2, and Microsoft SQL Server. Other tables use that identifier to provide "relational" data links and results. These models work based on the idea that each table setup will include a primary key or identifier. The relational data model describes the world as “a collection of inter-related relations (or tables).” A relational data model involves the use of data tables that collect groups of elements into relations. Currently, it is the most widely used data model. The relational data model was introduced by C.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
